In our example, the sales revenue from one shirt is \(\$15\) and the variable cost of one shirt is \(\$10\), so the individual contribution margin is \(\$5\). This \(\$5\) contribution margin is assumed to first cover fixed costs first and then realized as profit. The contribution margin measures how efficiently a company can produce products and maintain low levels of variable costs. It is considered a managerial ratio because companies rarely report margins to the public.
What Is the Difference Between Contribution Margin and Profit Margin?
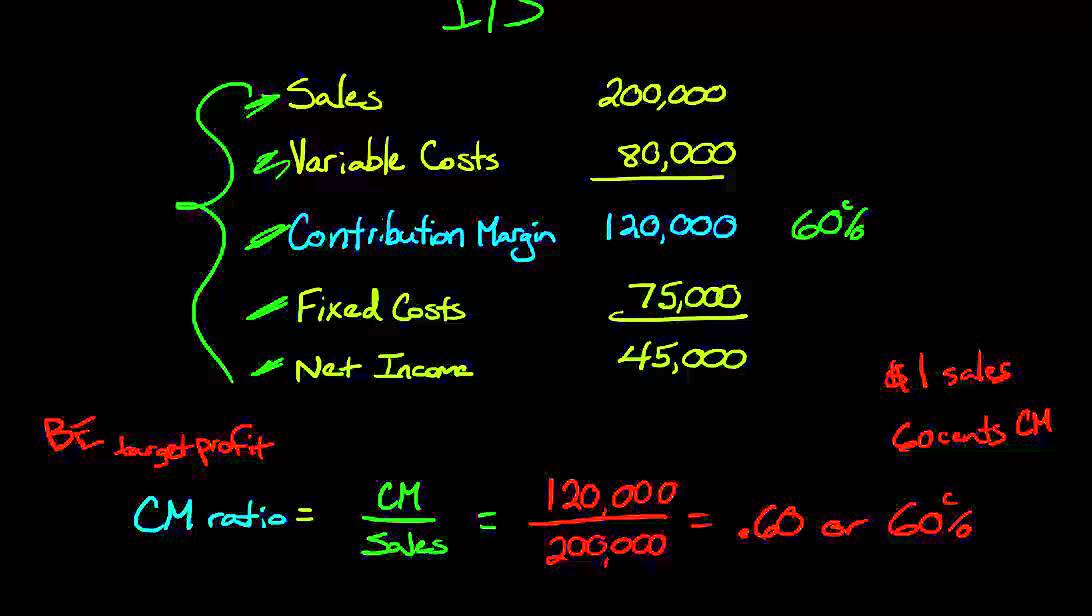
The electricity expenses of using ovens for baking a packet of bread turns out to be $1. Should the product be viewed as more of a “loss leader” or a “marketing” expense? Management should also use different types of inventory variations of the CM formula to analyze departments and product lines on a trending basis like the following. The 60% CM ratio implies the contribution margin for each dollar of revenue generated is $0.60.
Fixed Cost vs. Variable Cost
As a manager, you may be asked to negotiate or talk with vendors and perhaps even to ask for discounts. Small differences in prices of your supplies can make a huge difference in the profitability of a company. There is no definitive answer to this question, as it will vary depending on the specific business and its operating costs.
Contribution Margin Per Unit Formula:
Net sales refer to the total revenue your business generates as a result of selling its goods or services. Contribution Margin refers to the amount of money remaining to cover the fixed cost of your business. That is, it refers to the additional money that your business generates after deducting the variable costs of manufacturing your products. As mentioned earlier, the contribution margin ratio can help businesses determine the lowest possible price at which sales can be made and still break even. This analysis can aid in setting prices, planning sales or discounts, and managing additional costs like delivery fees.

The contribution margin is important because it gives you a clear, quick picture of how much “bang for your buck” you’re getting on each sale. It offers insight into how your company’s products and sales fit into the bigger picture of your business. If the contribution margin for a particular product is low or negative, it’s a sign that the product isn’t helping your company make a profit and should be sold at a different price point or not at all. It’s also a helpful metric to track how sales affect profits over time. Let’s say we have a company that produces 100,000 units of a product, sells them at $12 per unit, and has a variable costs of $8 per unit.
How can a business increase its Contribution Margin Ratio?
Fixed costs are one-time purchases for things like machinery, equipment or business real estate. Aside from the uses listed above, the contribution margin’s importance also lies in the fact that it is one of the building blocks of break-even analysis. With that all being said, it is quite obvious why it is worth learning the contribution margin formula. You need to fill in the following inputs to calculate the contribution margin using this calculator. Accordingly, the per-unit cost of manufacturing a single packet of bread consisting of 10 pieces each would be as follows.
The result of this calculation shows the part of sales revenue that is not consumed by variable costs and is available to satisfy fixed costs, also known as the contribution margin. The break even point (BEP) is the number of units at which total revenue (selling price per unit) equals total cost (fixed costs + variable cost). If the selling price per unit is more than the variable cost, it will be a profitable venture otherwise it will result in loss. Using this formula, the contribution margin can be calculated for total revenue or for revenue per unit. For instance, if you sell a product for $100 and the unit variable cost is $40, then using the formula, the unit contribution margin for your product is $60 ($100-$40). This $60 represents your product’s contribution to covering your fixed costs (rent, salaries, utilities) and generating a profit.
Furthermore, sales revenue can be categorized into gross and net sales revenue. Fixed costs are the costs that do not change with the change in the level of output. In other words, fixed costs are not dependent on your business’s productivity. Furthermore, an increase in the contribution margin increases the amount of profit as well. Furthermore, it also gives you an understanding of the amount of profit you can generate after covering your fixed cost.
- The contribution margin ratio of a business is the total revenue of the business minus the variable costs, divided by the revenue.
- If you need to estimate how much of your business’s revenues will be available to cover the fixed expenses after dealing with the variable costs, this calculator is the perfect tool for you.
- To convert the contribution margin into the contribution margin ratio, we’ll divide the contribution margin by the sales revenue.
- This is because the breakeven point indicates whether your company can cover its fixed cost without any additional funding from outside financiers.
It also helps management understand which products and operations are profitable and which lines or departments need to be discontinued or closed. The contribution margin is the leftover revenue after variable costs have been covered and it is used to contribute to fixed costs. If the fixed costs have also been paid, the remaining revenue is profit. High CM ratios are generally desirable because they indicate that a large portion of each sale contributes to covering fixed costs and profit. However, it is also essential to balance this with the level of fixed costs – a business with high fixed costs will need a higher CM ratio to break even.
Understanding and applying this concept, helps enable businesses to make informed decisions that can enhance profitability and long-term success. As you can see, contribution margin is an important metric to calculate and keep in mind when determining whether to make or provide a specific product or service. They can use that information to determine whether the company prices its products accurately or is likely to turn a profit without looking at that company’s balance sheet or other financial information. You can use contribution margin to help you make intelligent business decisions, especially concerning the kinds of products you make and how you price those products. Imagine that you have a machine that creates new cups, and it costs $20,000.

