In the United States, similar labor-saving processes have been developed, such as the ability to order groceries or fast food online and have it ready when the customer arrives. Do these labor-saving processes change the cost structure for the company? The concept of this equation relies on the difference between fixed and variable costs.
How does the contribution margin affect profit?
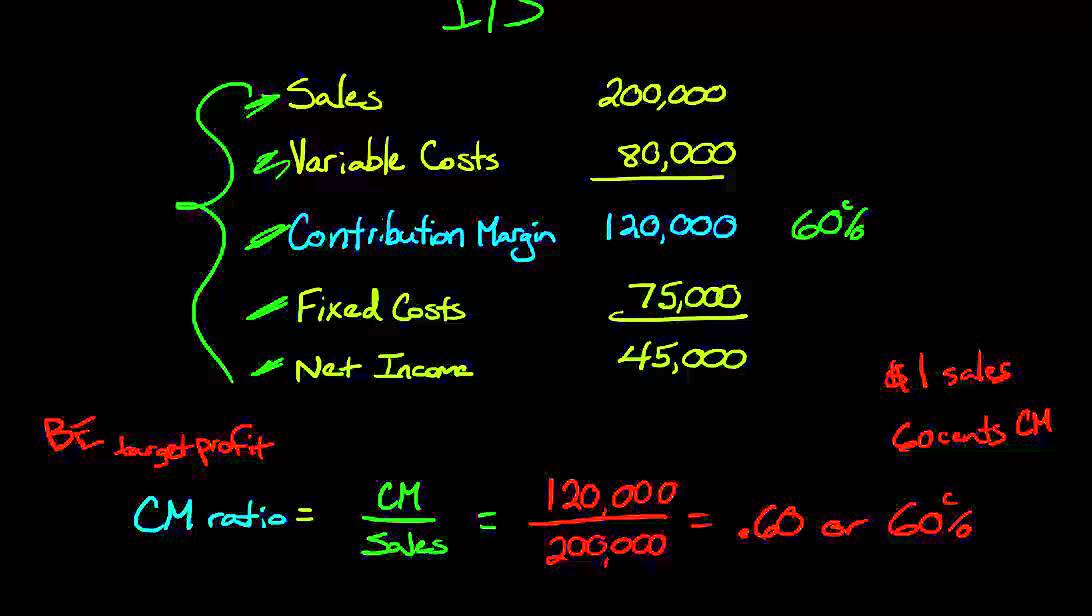
Knowing how to calculate contribution margin allows us to move on to calculating the contribution margin ratio. To get the ratio, all you need to do is divide the contribution margin by the total revenue. Thus, the concept of contribution margin is used to determine the minimum price at which you should sell your goods or services to cover its costs. Therefore, it is not advised to continue selling your product if your contribution margin ratio is too low or negative. This is because it would be quite challenging for your business to earn profits over the long-term.
What other financial metrics are related to the Contribution Margin Ratio?
You might wonder why a company would trade variable costs for fixed costs. One reason might be to meet company goals, such as gaining market share. Other reasons include being a leader in the use of innovation and basic accounting principles and concepts for t improving efficiencies. If a company uses the latest technology, such as online ordering and delivery, this may help the company attract a new type of customer or create loyalty with longstanding customers.
- Crucial to understanding contribution margin are fixed costs and variable costs.
- It is important to note that this unit contribution margin can be calculated either in dollars or as a percentage.
- To run a company successfully, you need to know everything about your business, including its financials.
- Below is a breakdown of contribution margins in detail, including how to calculate them.
- Profits will equal the number of units sold in excess of 3,000 units multiplied by the unit contribution margin.
The Formula and Result

So, you should produce those goods that generate a high contribution margin. As a result, a high contribution margin would help you in covering the fixed costs of your business. For example, in sectors with high fixed costs, such as those with hefty capital investments or sizable research and development expenditures, a higher contribution margin ratio may be needed to achieve viability. Other financial metrics related to the Contribution Margin Ratio include the gross margin ratio, operating margin ratio, and net profit margin ratio.
As you will learn in future chapters, in order for businesses to remain profitable, it is important for managers to understand how to measure and manage fixed and variable costs for decision-making. In this chapter, we begin examining the relationship among sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profit in decision-making. We will discuss how to use the concepts of fixed and variable costs and their relationship to profit to determine the sales needed to break even or to reach a desired profit.
Operating Profit or Loss
For example, a company aspiring to offer free delivery should achieve a scale where such an offering doesn’t negatively impact profits. A business can increase its Contribution Margin Ratio by reducing the cost of goods sold, increasing the selling price of products, or finding ways to reduce fixed costs. A high Contribution Margin Ratio indicates that each sale produces more profit than it did before and that the business will have an easier time making up fixed costs. A low Contribution Margin Ratio, on the other hand, suggests that there may be difficulty in covering fixed costs and making profits due to lower margins on individual sales.
Such fixed costs are not considered in the contribution margin calculations. Thus, the level of production along with the contribution margin are essential factors in developing your business. Now, it is essential to divide the cost of manufacturing your products between fixed and variable costs.
It is the monetary value that each hour worked on a machine contributes to paying fixed costs. You work it out by dividing your contribution margin by the number of hours worked on any given machine. Use contribution margin alongside gross profit margin, your balance sheet, and other financial metrics and analyses. This is the only real way to determine whether your company is profitable in the short and long term and if you need to make widespread changes to your profit models. Reduce variable costs by getting better deals on raw materials, packaging, and shipping, finding cheaper materials or alternatives, or reducing labor costs and time by improving efficiency.
Put more simply, a contribution margin tells you how much money every extra sale contributes to your total profits after hitting a specific profitability point. This is because the breakeven point indicates whether your company can cover its fixed cost without any additional funding from outside financiers. The following are the steps to calculate the contribution margin for your business. And to understand each of the steps, let’s consider the above-mentioned Dobson example.

